4 Types Of Water Erosion
Erosion
Worldwide, 26.4 billion tons of soil is lost each yr. This rate is ten times higher than the natural charge per unit.
Fifty-fifty though erosion is a natural phenomenon, human interference into natural systems have created erosion that is much higher than the boilerplate geological erosion rate. Erosion is a threat to sustained agricultural product. Soil erosion is a process of moving soil by h2o or wind - when the soil particles are discrete and transported to a different location. This is a natural process that has occurred for eons of time. Water, wind, ice, and gravity are involved in moving soil materials. Humans, however, accept often acquired accelerated erosion by our manipulation of the soil for agriculture or construction use. When soils are left bare even for a brusk period (such equally when fields are tilled for planting), the soil tin be picked upward and moved. These bare soil drops are exposed to the free energy of the raindrops and air current. The finer particles of soil are eroded first, taking with them most of the natural fertility and product potential. Yet, with plant comprehend, the roots bind the soil particles together and lesson erosion.
Erosion involved three processes: detachment (from the ground), transportation (via water or wind), and deposition. The deposition is ofttimes in places we don't want the soil such as streams, lakes, reservoirs, or deltas. And, of concern is that the topsoil is often the virtually fertile and when information technology erodes away, the subsoil is less productive.
Water Erosion

Water is powerful! Water erosion is caused by ii master forces - raindrop impact and flowing water. Raindrops can both destroy soil aggregates and send soil small distances. So, flowing water transports these discrete particles downwardly hill. The size of the particles transported increases with the kinetic free energy of the water. The deeper the h2o is, the larger the particles that move. These particles move away from the field, and end upwardly in streams and waterways.

Three types of water erosion can occur, sheet, rill, and gully.
- Sheet erosion: This erosion is the hardest to see, as a compatible soil layer is removed from an surface area over the surface.
- Rill erosion: This type of erosion starts as water flowing over the soil surface concentrates into small streams, creating channels of water menstruum.
- Gully erosion: If the rill erosion is non kept nether control, it creates gullies, which are deeper and wider cuts. They are really problematic on cropland, since tractors and tillage implements cannot get across them.
Current of air Erosion
Soil can make full the air when it is dry and not anchored by vegetation. Recall dorsum to the Dust Bowl of the 1930s, which is i of the biggest environmental disasters in United States history. The inversion of soils burying resides left the surface blank. When the rains didn't come, the atmospheric condition were ready for disaster. The winds came and lifted the bare soils into the heaven over 10,000 feet two to three times a week. This ended afterward 10 years. The development of irrigation and encompass decreased erosion past the time the 1950s came forth. The less amount of atmospheric precipitation in the Western not bad plains yet creates more air current erosion, because they get less atmospheric precipitation and has lower amounts of vegetation. There are also less trees and they are flatter. The soils are lower in organic matter, which acts as a glue to hold soil clumps together.

Dust blown past the wind from an Iowa field that was not planted to grass to prevent soil erosion in 1890. Credit: National Archives and Records Administration.
Sands actually start the wind erosion process. They are round and become lifted into the air like plane wings. These moving particles knock the clay and silt loose into the air, where they can go several g kilometers. Similar water erosion, in that location are three different types of wind erosion, surface creep, saltation, and suspension.
Surface Creep: When the wind speed at the soil surface exceeds 13 miles per hour (21 kilometers per hr), soil particles start to roll along the soil surface.
Saltation: As the wind speeds pick upwardly, the surface particles kickoff leaping off the surface into the air, this procedure is saltation.
Suspension: Afterwards the saltation begins, the particles hit the surface and knock loose other particles, knocking them into the air. These include smaller sand particles and clays. They then are lifted into the atmosphere and tin can be transported long distances until the wind speed decreases.
Controlling Erosion
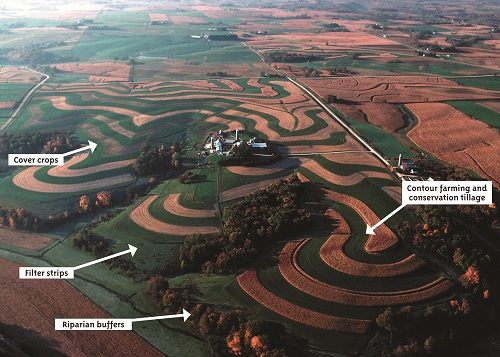
Wise employ of our soils requires u.s. to minimize erosion. The best fashion to command water erosion involve slowing downwards the menses of water and limiting soil disengagement. The best fashion to prevent this is to keep the soil covered with either growing plants or residues from past crops. These blot the energy from raindrops and irksome the rate of water flow over the surface, allowing more time to have water infiltrate through the soil. Cultivation is very important in agronomics, only there are several best management practices that can help reduce erosion. Using encompass crops, filter strips, contour farming and conservation tillage, and riparian buffers can help reduce or eliminate soil movement. Minimum and no till systems help with both types of erosion.
Boosted Resources
Erosion Facts and Conservation![]()
H2o Erosion and Conservation![]()
Wind Erosion and Conservation![]()
Go back to the Soil/Human Interactions page
4 Types Of Water Erosion,
Source: https://www.soils4teachers.org/erosion
Posted by: gentrysaughts1992.blogspot.com


0 Response to "4 Types Of Water Erosion"
Post a Comment